Tutorial: Tracing code
Indeed, the ratio of time spent reading versus writing is well over 10 to 1. We are constantly reading old code as part of the effort to write new code. …[Therefore,] making it easy to read makes it easier to write.
— Robert C. Martin Clean Code: A Handbook of Agile Software Craftsmanship
When trying to understand an unfamiliar code base, one common strategy used is to trace some representative execution path through the code base. One easy way to trace an execution path is to use a debugger to step through the code. In this tutorial, you will be using the IntelliJ IDEA’s debugger to trace the execution path of a specific user command.
Before we start
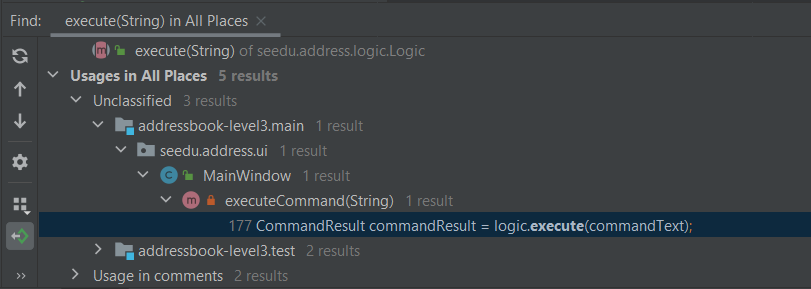
Before we jump into the code, it is useful to get an idea of the overall structure and the high-level behavior of the application. This is provided in the 'Architecture' section of the developer guide. In particular, the architecture diagram (reproduced below), tells us that the App consists of several components.
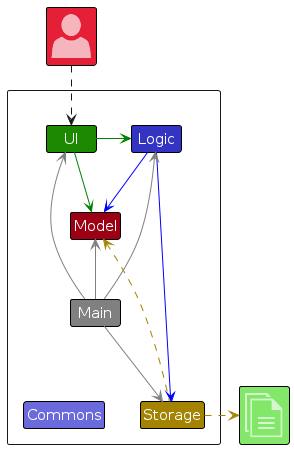
It also has a sequence diagram (reproduced below) that tells us how a command propagates through the App.
Note how the diagram shows only the execution flows between the main components. That is, it does not show details of the execution path inside each component. By hiding those details, the diagram aims to inform the reader about the overall execution path of a command without overwhelming the reader with too much details. In this tutorial, you aim to find those omitted details so that you get a more in-depth understanding of how the code works.
Before we proceed, ensure that you have done the following:
- Read the Architecture section of the DG
- Set up the project in Intellij IDEA
- Learn basic debugging features of Intellij IDEA
- If you are using a different IDE, we'll leave it to you to figure out the equivalent feature to use in your IDE.
- If you are not using an IDE, we'll let you figure out how to achieve the same using your coding toolchain.
Setting a breakpoint
As you know, the first step of debugging is to put in a breakpoint where you want the debugger to pause the execution.
For example, if you are trying to understand how the App starts up, you would put a breakpoint in the first statement of
the main method.
In our case, we would want to begin the tracing at the very point where the App start processing user input (i.e.,
somewhere in the UI component), and then trace through how the execution proceeds through the UI component. However, the
execution path through a GUI is often somewhat obscure due to various event-driven mechanisms used by GUI frameworks,
which happens to be the case here too. Therefore, let us put the breakpoint where the UI transfers control to
the Logic component.

According to the sequence diagram you saw earlier (and repeated above for reference), the UI component yields control
to the Logic component through a method named execute. Searching through the code base for an execute() method
that belongs to the Logic component yields a promising candidate in seedu.address.logic.Logic.
Intellij Tip: The 'Search Everywhere' feature
can be used here. In particular, the 'Find Symbol' ('Symbol' here refers to methods, variables, classes etc.)
variant of that feature is quite useful here as we are looking for a method named execute, not simply the
text execute.
A quick look at the seedu.address.logic.Logic (an extract given below) confirms that this indeed might be what we’re
looking for.
public interface Logic {
/**
* Executes the command and returns the result.
* @param commandText The command as entered by the user.
* @return the result of the command execution.
* @throws CommandException If an error occurs during command execution.
* @throws ParseException If an error occurs during parsing.
*/
CommandResult execute(String commandText) throws CommandException, ParseException;
...
}
But apparently, this is an interface, not a concrete implementation. That should be fine because the Architecture section of the Developer Guide tells us that components interact through interfaces. Here's the relevant diagram:
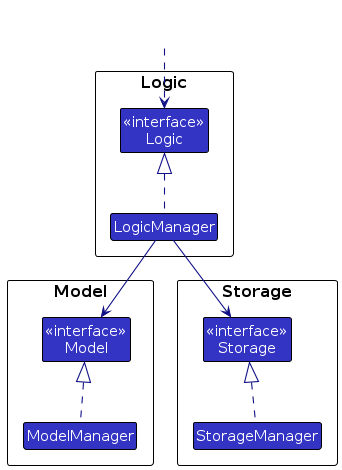
Next, let's find out which statement(s) in the UI code is calling this method, thus transferring control from the UI
to the Logic.
Intellij Tip: The 'Find Usages' feature can find from which parts of the code a class/method/variable is being used.
Bingo! MainWindow#executeCommand() seems to be exactly what we’re looking for!
Now let’s set the breakpoint. First, double-click the item to reach the corresponding code. Once there, click on the
left gutter to set a breakpoint, as shown below.
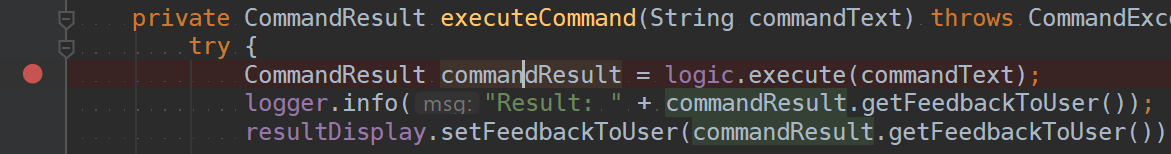
Tracing the execution path
Recall from the User Guide that the edit command has the
format: edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG]… For this tutorial we will be issuing the
command edit 1 n/Alice Yeoh.
Tip: Over the course of the debugging session, you will encounter every major component in the application. Try to keep track of what happens inside the component and where the execution transfers to another component.
To start the debugging session, simply
Run>Debug MainWhen the GUI appears, enter
edit 1 n/Alice Yeohinto the command box and pressEnter.The Debugger tool window should show up and show something like this:
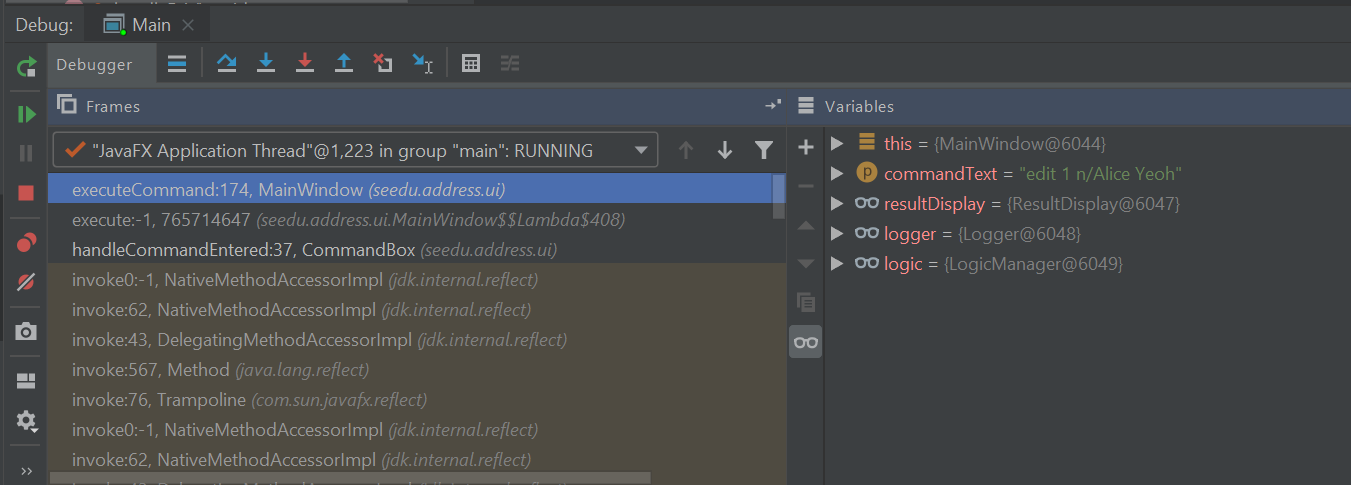
Use the Show execution point feature to jump to the line of code that we stopped at:
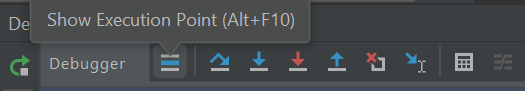
CommandResult commandResult = logic.execute(commandText);is the line that you end up at (i.e., the place where we put the breakpoint).We are interested in the
logic.execute(commandText)portion of that line so let’s Step in into that method call:
We end up in
LogicManager#execute()(notLogic#execute-- but this is expected because we know theexecute()method in theLogicinterface is actually implemented by theLogicManagerclass). Let’s take a look at the body of the method. Given below is the same code, with additional explanatory comments.LogicManager#execute().
@Override public CommandResult execute(String commandText) throws CommandException, ParseException { //Logging, safe to ignore logger.info("----------------[USER COMMAND][" + commandText + "]"); CommandResult commandResult; //Parse user input from String to a Command Command command = addressBookParser.parseCommand(commandText); //Executes the Command and stores the result commandResult = command.execute(model); try { //We can deduce that the previous line of code modifies model in some way // since it's being stored here. storage.saveAddressBook(model.getAddressBook()); } catch (IOException ioe) { throw new CommandException(FILE_OPS_ERROR_MESSAGE + ioe, ioe); } return commandResult; }LogicManager#execute()appears to delegate most of the heavy lifting to other components. Let’s take a closer look at each one.Step over the logging code since it is of no interest to us now.
Step into the line where user input in parsed from a String to a Command, which should bring you to the
AddressBookParser#parseCommand()method (partial code given below):public Command parseCommand(String userInput) throws ParseException { ... final String commandWord = matcher.group("commandWord"); final String arguments = matcher.group("arguments"); ...Step over the statements in that method until you reach the
switchstatement. The 'Variables' window now shows the value of bothcommandWordandarguments:
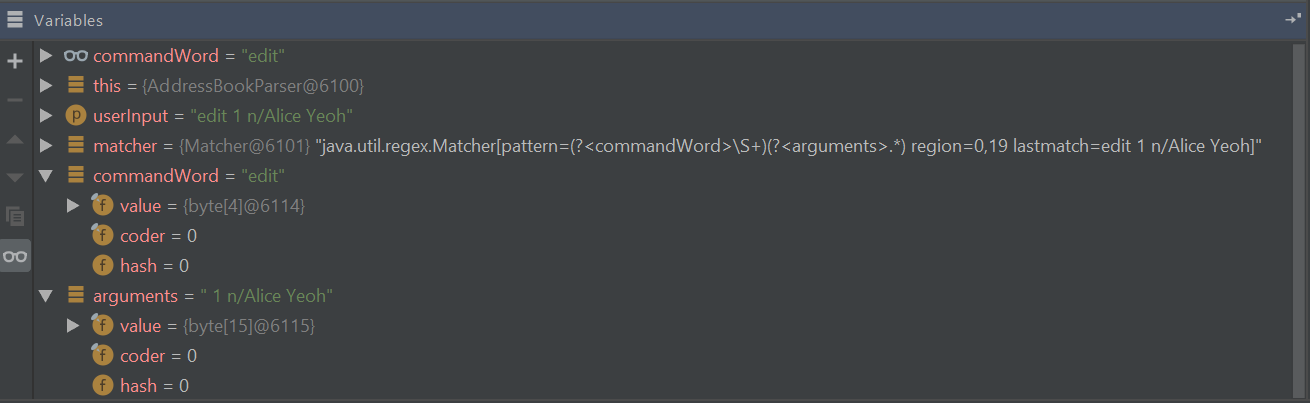
We see that the value of
commandWordis noweditbutargumentsis still not processed in any meaningful way.Stepping through the
switchblock, we end up at a call toEditCommandParser().parse()as expected (because the command we typed is an edit command).... case EditCommand.COMMAND_WORD: return new EditCommandParser().parse(arguments); ...Let’s see what
EditCommandParser#parse()does by stepping into it. You might have to click the 'step into' button multiple times here because there are two method calls in that statement:EditCommandParser()andparse().Intellij Tip: Sometimes, you might end up stepping into functions that are not of interest. Simply use the
step outbutton to get out of them!Stepping through the method shows that it calls
ArgumentTokenizer#tokenize()andParserUtil#parseIndex()to obtain the arguments and index required.The rest of the method seems to exhaustively check for the existence of each possible parameter of the
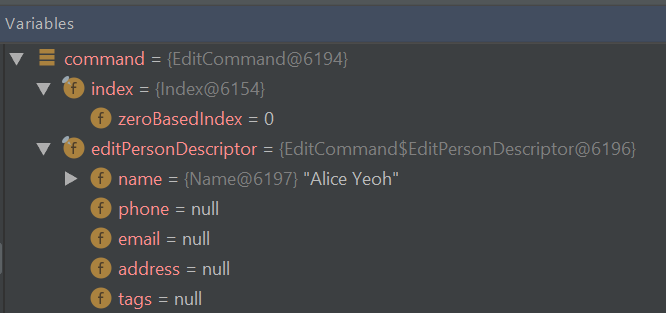
editcommand and store any possible changes in anEditPersonDescriptor. Recall that we can verify the contents ofeditPersonDesciptorthrough the 'Variables' window.
As you just traced through some code involved in parsing a command, you can take a look at this class diagram to see where the various parsing-related classes you encountered fit into the design of the
Logiccomponent.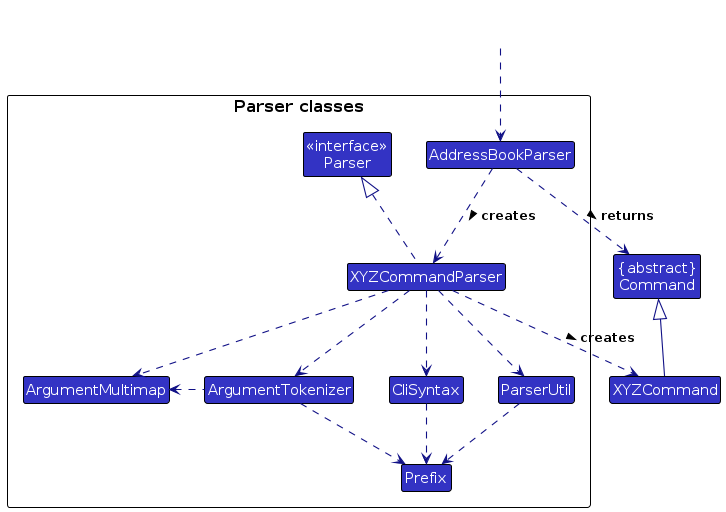
Let’s continue stepping through until we return to
LogicManager#execute().The sequence diagram below shows the details of the execution path through the Logic component. Does the execution path you traced in the code so far match the diagram?
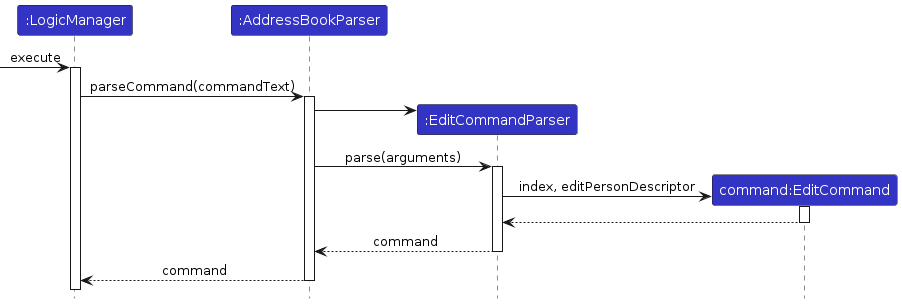
Now, step over until you read the statement that calls the
execute()method of theEditCommandobject received, and step into thatexecute()method (partial code given below):EditCommand#execute():@Override public CommandResult execute(Model model) throws CommandException { ... Person customerToEdit = lastShownList.get(index.getZeroBased()); Person editedCustomer = createEditedPerson(customerToEdit, customerEditDescriptor); if (!customerToEdit.isSamePerson(editedCustomer) && model.hasPerson(editedCustomer)) { throw new CommandException(MESSAGE_DUPLICATE_PERSON); } model.setPerson(customerToEdit, editedCustomer); model.updateFilteredPersonList(PREDICATE_SHOW_ALL_PERSONS); return new CommandResult(String.format(MESSAGE_EDIT_PERSON_SUCCESS, editedCustomer)); }As suspected,
command#execute()does indeed make changes to themodelobject. Specifically,- it uses the
setPerson()method (defined in the interfaceModeland implemented inModelManageras per the usual pattern) to update the customer data. - it uses the
updateFilteredPersonListmethod to ask theModelto populate the 'filtered list' with all customers.
FYI, The 'filtered list' is the list of customers resulting from the most recent operation that will be shown to the user immediately after. For theeditcommand, we populate it with all the customers so that the user can see the edited customer along with all other customers. If this was afindcommand, we would be setting that list to contain the search results instead.
To provide some context, given below is the class diagram of theModelcomponent. See if you can figure out where the 'filtered list' of customers is being tracked.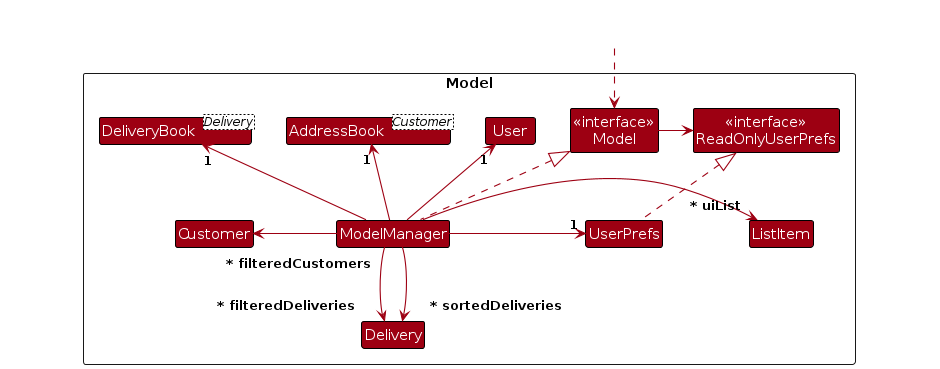
- 💡 This may be a good time to read through
the
Modelcomponent section of the DG
- it uses the
As you step through the rest of the statements in the
EditCommand#execute()method, you'll see that it creates aCommandResultobject (containing information about the result of the execution) and returns it.
Advancing the debugger by one more step should take you back to the middle of theLogicManager#execute()method.Given that you have already seen quite a few classes in the
Logiccomponent in action, see if you can identify in this partial class diagram some of the classes you've encountered so far, and see how they fit into the class structure of theLogiccomponent: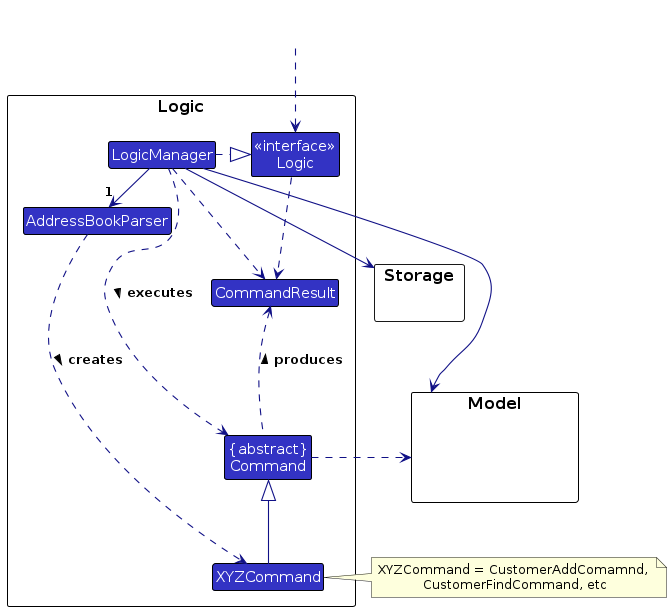
- 💡 This may be a good time to read through
the
Logiccomponent section of the DG
- 💡 This may be a good time to read through
the
Similar to before, you can step over/into statements in the
LogicManager#execute()method to examine how the control is transferred to theStoragecomponent and what happens inside that component.Intellij Tip: When trying to step into a statement such as
storage.saveAddressBook(model.getAddressBook())which contains multiple method calls, Intellij will let you choose (by clicking) which one you want to step into.As you step through the code inside the
Storagecomponent, you will eventually arrive at theJsonAddressBook#saveAddressBook()method which calls theJsonSerializableAddressBookconstructor, to create an object that can be serialized (i.e., stored in storage medium) in JSON format. That constructor is given below ( with added line breaks for easier readability):JsonSerializableAddressBookconstructor:/** * Converts a given {@code ReadOnlyAddressBook} into this class for Jackson use. * * @param source future changes to this will not affect the created * {@code JsonSerializableAddressBook}. */ public JsonSerializableAddressBook(ReadOnlyAddressBook source) { customers.addAll( source.getPersonList() .stream() .map(JsonAdaptedPerson::new) .collect(Collectors.toList())); }It appears that a
JsonAdaptedPersonis created for eachPersonand then added to theJsonSerializableAddressBook. This is because regular Java objects need to go through an adaptation for them to be suitable to be saved in JSON format.While you are stepping through the classes in the
Storagecomponent, here is the component's class diagram to help you understand how those classes fit into the structure of the component.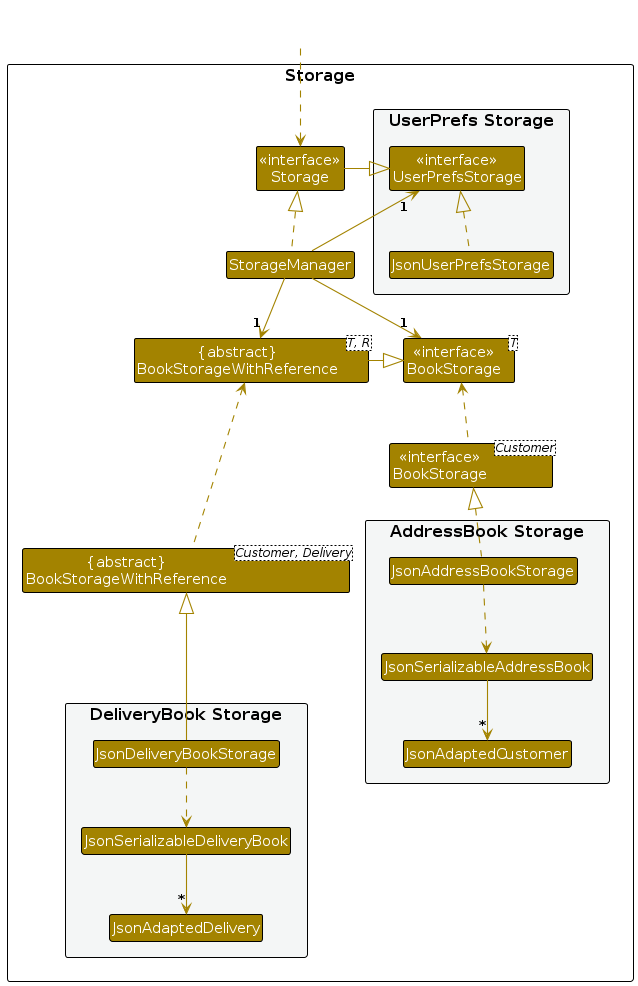
- 💡 This may be a good time to read through
the
Storagecomponent section of the DG
- 💡 This may be a good time to read through
the
We can continue to step through until you reach the end of the
LogicManager#execute()method and return to theMainWindow#executeCommand()method (the place where we put the original breakpoint).Stepping into
resultDisplay.setFeedbackToUser(commandResult.getFeedbackToUser());, we end up in:ResultDisplay#setFeedbackToUser()public void setFeedbackToUser(String feedbackToUser) { requireNonNull(feedbackToUser); resultDisplay.setText(feedbackToUser); }Finally, you can step through until you reach the end of
MainWindow#executeCommand().
💡 This may be a good time to read through theUIcomponent section of the DG
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we traced a valid edit command from raw user input to the result being displayed to the user. From this tutorial, you learned more about how the various components work together to produce a response to a user command.
Here are some quick questions you can try to answer based on your execution path tracing. In some cases, you can do further tracing for the given commands to find exactly what happens.
In this tutorial, we traced the "happy path" (i.e., no errors). What do you think will happen if we traced the following commands instead? What exceptions do you think will be thrown (if any), where will the exceptions be thrown and where will they be handled?
redit 1 n/Alice Yuedit 0 n/Alice Yuedit 1 n/Alex Yeohedit 1edit 1 n/アリス ユーedit 1 t/one t/two t/three t/one
What components will you have to modify to perform the following enhancements to the application?
Make command words case-insensitive
Allow
deleteto remove more than one index at a timeSave the address book in the CSV format instead
Add a new command
Add a new field to
PersonAdd a new entity to the address book